What is the placenta?
A few weeks ago, during a consultation at my office, I asked a woman who was 7 months pregnant if she had any questions. We had just talked about everything and anything and I hoped that I had given her enough confidence to ask me all the questions, as "stupid" as they were (for her, because there are never stupid questions, especially when it comes to pregnancy). She then asked me:
"what is the placenta?"
The whole medical profession will talk to you about the placenta and this from the first ultrasound. They will say, "Oh, it's too low, you have to stay in bed" or "Oh, everything is fine" or "There is a retro placental hematoma", etc. But I realized that in reality, at no time did we explain to women and their spouses what this famous placenta was.
What is the placenta?
The placenta is an incredible organ. Yes, you read that right, an organ! What makes it fascinating is that it is temporary. It exists only for the duration of the pregnancy.
It is composed of a maternal part (the endometrium) but also of a part of the embryo (the trophoblast).
It is formed as soon as the embryo is implanted (from the 6th day) but is not functional until the 3rd month. It is completely formed at the 5th month.
- Appearance: smooth and shiny
- Weight : 500 to 600 g
- Diameter: between 16 and 20 cm
What is the purpose of the placenta?
The placenta provides the link between the mother and the fetus.
Nutrition
It allows the nutrition of the fetus.
Oxygenation
It also allows oxygenation.
The hormones
It is the placenta that secretes HCG, the hormone specific to pregnant women, as soon as it appears. Its presence in the blood or urine tells you that you are pregnant. The placenta is also responsible for the secretion of estrogen and progesterone.
Protection and filter: not for everything!
The placenta has a protective role against infections. It also regulates the passage of certain medications. We remind you to follow your doctor's advice and to read the instructions of the medication before taking anything. The same is true for alcohol and drugs, which are not filtered by the placenta.
Waste disposal
The placenta also has the role of eliminating organic waste that is produced by the baby such as CO2 and urine, carbon dioxide.
Delivery: the expulsion of the placenta
About 30 minutes after the baby comes out, it is the placenta's turn to come out.
Why does the midwife examine the placenta after delivery?
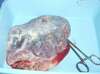
It is essential to examine the placenta once it has come out.
Prevent or treat postpartum hemorrhage (delivery hemorrhage)
The first reason is to check if it is complete. Indeed, it is possible that a piece of placenta remained inside the mother's body. This piece will continue to bleed because it connects the mother to the baby, so it connects the mother and more particularly the blood of the mother to nothing... It's like a pipe but it's not blocked. So there is a big risk ofhemorrhage. This is also the reason why in the hours following your delivery, the midwives will lift your sheets several times to check that you are not bleeding. In the event that a piece of the baby is left behind, you must go and get it. To do this, 2 techniques are possible:
- Uterine revision: for this technique, the gynecologist or midwife will place his or her hand and forearm inside the patient and move around the uterus to remove any small piece of placenta. This technique is not pleasant for the patients and not always well received, however, it is essential to avoid complications.
- Surgery: when uterine revision is not possible or is not sufficient to detect the origin of the bleeding, surgery may be performed.
Placenta examination also helps to explain certain pathologies of pregnancy, childbirth, infections or even certain malformations.
Placental anomalies
Placenta praevia
Placenta previa is when the placenta is too close to the cervix. It can be quite common to have a placenta previa in early pregnancy and the placenta can come up on its own. In cases of placenta previa, we recommend that the pregnant woman lie down as much as possible.
The problem with placenta previa is that the placenta (the baby's nourishing organ) must not come out before the baby. This is why when the mother-to-be has a placenta previa at the end of her pregnancy, a caesarean section is systematically scheduled.
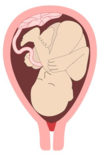
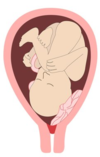
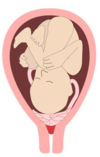
Placenta accreta
A placenta acheta is a placenta that has been inserted too deeply into the muscular layer of the uterus called the myometrium. The problem lies in the fact that during delivery, the placenta must be expelled but it may remain attached to the wall of the uterus.
There are 3 forms of placenta accreta:
- placenta accreta: it is inserted into the superficial part of the wall of the uterus
- placenta increta: it invades the wall of the uterus in depth, sometimes the entire wall
- placenta percreta: it invades territories outside the uterus and can therefore affect neighboring organs.
Retroplacental hematoma
It is possible to have a hematoma behind the placenta, which can cause bleeding. This hematoma may resolve on its own, but it can also detach the placenta.
Retroplacental hematoma in the third trimester is an absolute obstetrical emergency.
The patient's symptoms are:
- Abrupt abdominal pain called thunderclap.
- 30% of metrorrhagia (bleeding) in the third trimester is related to this hematoma.
The main risk factor is gestational hypertension with or without pre-eclampsia. But it can occur spontaneously or by being provoked as for example during a fall.

Marie Messager
Osteopath D.O
2 rue Alexis de Tocqueville
78000 Versailles



