Golf elbow or epitrochleitis and osteopathy
What is golf elbow or epitrochleitis?
Golf elbow, also called epitrochleitis or medial epicondylitis, is an internal tendinopathy of the elbow. This condition is 5 times less frequent than epicondylitis, also called tennis elbow.
The tendon affected in epitrochleitis is a common tendon between Superficial Common Flexor of the fingers, Palmaris longus, Radial Flexor of the Carpus, Ulnar Flexor of the Carpus, pronator ring.
Due to overuse of these muscles, the common tendon will suffer micro lesions and a reshaping of its structure.
Who gets golf elbow?

- Golfers especially beginners or those who intensify their practice in one shot.
- But also tennis players throwing javelins, and in other throws.
Epitrochelitis Clinic:
- Pain on the inside of the elbow
- Pain reproduced on palpation of the medial condyle
- Pain of progressive onset following the repetition of movement
- Pain occurring when bending the elbow, or when clenching the fist, such as when shaking hands.
Causes of medial epicondylitis:
- Lack or absence of warm-up
- Bad technique: the repetition of a badly performed gesture repeated many times can be a source of tendinopathy
- Overtraining or recovery too fast

Specific to golfers:
- Unsuitable equipment:
-
- Heavy or stiff golf clubs
- A grip that is too small or too big: if the grip is not adapted, the player will not hold the club properly, which can lead to tendinopathy.
-
- Tensions about the club
- Overtraining, especially at the driving range.
Complementary examinations of golf elbow:
Ultrasound can highlight enthesopathies related to this pathology, we will then find on ultrasound :
- Thickening of the tendon
- Loss of the fibrillar structure
- Sometimes calcifications in chronic forms
X-rays are useless for tennis elbow unless they are used to rule out something else. MRI could show epitrochleitis but ultrasound, which is much cheaper, is sufficient.
Golf elbow treatment
The management of golf elbow must be multidisciplinary and requires the commitment of the patient.
Relative rest
Stopping golf or at least adapting the physical activity must be applied. It is not necessary to rest completely, it is necessary to work the tendon but without loads. The aim is to work the tendon fibers gently so that they do not rebuild themselves in an anarchic way, but they should not be overworked for fear of returning to an injury phase.
Osteopathy
Osteopathy is essential in the management of golf elbow. It is necessary to remove all the osteoarticular blockages that maintain the dysfunctions at the elbow level.
Your osteopath will therefore, thanks to a meticulous examination, understand the mechanical causes of this golf elbow. Then, thanks to precise and painless techniques, he will treat the dysfunctions, for example by working on the elbow joints, on the inter-bone membrane (between the two bones of the forearm), by acting directly on the tendon, etc.
Self-Massage
Massage the painful area of the elbow and move down the inside of the forearm.
Physiotherapy
The osteopath-physiotherapist collaboration is very useful to treat an elbow tendinopathy because they are two complementary approaches.
In order to treat golf elbow, the physical therapist may perform :
- Massages, especially deep transverse massages
- Shock waves
- Stretching
- Eccentric work of the muscles ++++ : this work should also be done by the patient at home.
Kinesiologist-taping
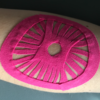
The kinesiotaping bands allow the resting of the tendon and to supplement it. They can be maintained for 5 days and are very useful during the treatment of the tendinopathy but also when resuming activity. These bands can be applied by a trained osteopath or another professional (physiotherapist, chiropractor) who has also followed a specific training.
Stretching of the common tendon
The useful stretch for golf elbow is to bring the elbow into extension and then the wrist into extension.

Marie Messager
Osteopath D.O
2 rue Alexis de Tocqueville
78000 Versailles



